자바에서의 큐
자료 구조 목차
- Data-Structure
- Linear
- Static
- Array
- Dynamic
- Linked List
- Stack
- Queue
- Static
- Non Linear
- Tree
- Graph
- Linear
자바에서의 큐 인터페이스에 대해
큐에 대한 개념을 알아보았으니 자바에서 사용되는 큐에 대해서 알아보자
큐 인터페이스는 java.util 패키지 안에 있으며 콜렉션 인터페이스에서 FIFO(First In First Out) 순으로 실행하는 요소들을 상속받고 있다.
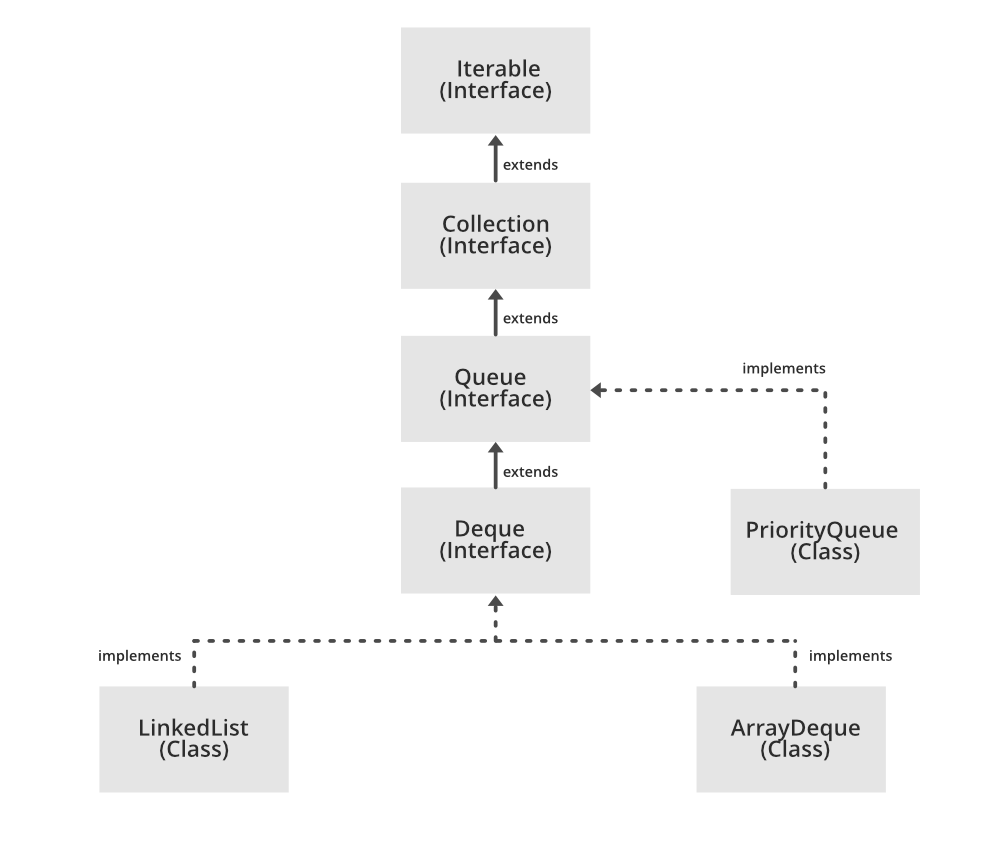
인터페이스임으로 큐는 선언을 위한 구현 클래스가 필요하다. 자주 사용되는 구현 클래스로는 PriorityQueue와 LinkedList가 있다. 참고로 이 클래스들은 thread safe하지 않습니다. 만약 thread safe가 필요하다면 PriorityBlockingQueue을 상속 받는 걸을 추천한다.
큐 객체 선언 및 생성
자바 1.5부터 소개된 제네릭이 생긴 이후부터큐에 어떤 타입의 객체를 담을건지 제한을 둘 수도 있다.
Queue<Obj> queue = new PriorityQueue<Obj>();
큐 예제(Linked List) :
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> integerQueue = new LinkedList<>();
// adds elements {0, 1, 2, 3, 4} to the queue
for (int i=0; i<5; i++) {
integerQueue.add(i);
}
// queue dispaly
System.out.println("Elements fo queue : " + integerQueue);
// remove the head of queue
int removedElement = integerQueue.remove();
System.out.println("removed element : " + removedElement);
System.out.println(integerQueue);
// view the head of queue
int head = integerQueue.peek();
System.out.println("head of queue : " + head);
int size = integerQueue.size();
System.out.println("Size of queue : " + size);
}
}
큐 인터페이스 명령어(PriorityQueue)
- 요소 더하기
import java.util.*;
public class QueueSample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<String> stringQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
stringQueue.add("Hello");
stringQueue.add("Java");
System.out.println(stringQueue);
}
}
- 요소 제거하기
import java.util.*;
public class QueueSample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<String> stringQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
stringQueue.add("Hello");
stringQueue.add("Java");
stringQueue.add("again");
System.out.println("Initial Queue : " + stringQueue);
stringQueue.remove("Hello");
System.out.println("After Remove : " + stringQueue);
System.out.println("Poll Method : " + stringQueue.poll());
System.out.println("Final Queue : " + stringQueue);
}
}
- 큐 내부 순회하기
import java.util.*;
public class QueueSample3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<String> stringQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
stringQueue.add("Hello");
stringQueue.add("Java");
stringQueue.add("!");
Iterator iterator = stringQueue.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterator.next() + "\t");
}
}
}
큐의 특성
- 큐에 요소를 삽입할 때는 큐 끝에 삽입되고 제거할 때는 큐 앞에서부터 제거된다. FIFO를 따른다.
- 자바 큐는 각종 콜렉션 인터페이스 메서드를 지원한다. 예로 insertion, deletion, etc.
LinkedList,ArrayBlockingQueue그리고PriorityQueue가 큐의 구현체 클래스로 자주 사용된다.- 만약
BlockingQueue메서드의 매개변수에 null 값이 들어가면 NullPointerException으로 처리된다. - java.util 패키지 안에 있는 큐는 무한(Unbounded) 큐이다.
- java.util.concurrent 패키지 안에 있는 큐는 유한(Bounded) 큐이다.
- 데크(Deque)를 제외한 모든 큐는 삽입은 head, 제거는 tail에서 하도록 지원된다. 데크는 양쪽에서 삽입과 제거가 가능하다.
큐 인터페이스 구현체 클래스
PriorityQueue:
PriorityQueue클래스는 우선 사항을 기반으로 수행하는 클래스이다. 큐는 FIFO 알고리즘으로 수행되지만 간혹 우선 순위에 따라서 실행해야하는 경우도 있다. 그때PriorityQueue를 사용해야한다.
import java.util.*;
class QueuePriorityQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating empty priority queue
Queue<Integer> integerQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
// Adding items to the integerQueue using add()
integerQueue.add(10);
integerQueue.add(20);
integerQueue.add(15);
// Printing the top element of the PriorityQueue
System.out.println(integerQueue.peek());
// Printing the top element and removing it from the Priorityqueue container
System.out.println(integerQueue.poll());
// Printing the top element again
System.out.println(integerQueue.peek());
}
}
LinkedList:
LinkedList는 콜렉션 프레임워크에서 연결 리스트 자료 구조를 상속받은 클래스이다. 요소가 연속적인 주소에 저장되지 않고 각 객체별로 데이터와 주소가 따로 저장되는 선형 자료 구조이다. 각 요소는 노드로 불리며 서로 포인터와 주소를 통해서 연결되어있다. 동적성과 쉬운 삽입 그리고 삭제로 인해 배열이나 큐보다 선호한다.
import java.util.*;
class QueueLinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating empty LinkedList queue
Queue<Integer> integerQueue = new LinkedList<>();
// Adding items to the integerQueue using add()
integerQueue.add(10);
integerQueue.add(20);
integerQueue.add(15);
// Printing the top element of the PriorityQueue
System.out.println(integerQueue.peek());
// Printing the top element and removing it from the LinkedList container
System.out.println(integerQueue.poll());
// Printing the top element again
System.out.println(integerQueue.peek());
}
}
PriorityBlockingQueue:
앞서 얘기한 것처럼PriorityQueue와LinkedList는 thread-safe하지 않다. 그렇기에 thread-safe 구현이 필요할 때에는PriorityBlockingQueue를 사용한다.PriorityBlockingQueue는PriorityQueue클래스의 특성을 따르면서 추가적으로 blocking retrieval operations을 제공한다.
import java.util.concurrent.PriorityBlockingQueue;
import java.util.*;
class QueuePriorityBlockingQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating empty priority blocking queue
Queue<Integer> integerQueue = new PriorityBlockingQueue<>();
// Adding items to the integerQueue using add()
integerQueue.add(10);
integerQueue.add(20);
integerQueue.add(15);
// Printing the top element of the PriorityBlockingQueue
System.out.println(integerQueue.peek());
// Printing the top element and removing it from the PriorityBlockingQueue
System.out.println(integerQueue.poll());
// Printing the top element again
System.out.println(integerQueue.peek());
}
}
간략하게 자바에서의 큐 인터페이스와 해당 구현체 클래스에 대해서 살짝 알아보았다.
다음은 언급한 PriorityQueue에 대해서 무엇인지 조금 더 알아보자그리고 사실 아직 배열, 연결 리스트, 스택, 큐라는 것에 대해서는 알겠어도 어디에 정확히 사용해야하는지는 잘 모르겠다… 자료 구조에 대해서 정리가 끝난 이후 알고리즘에 대해서 적으면서 알아보겠다.