큐
자료 구조 목차
- Data-Structure
- Linear
- Static
- Array
- Dynamic
- Linked List
- Stack
- Queue
- Static
- Non Linear
- Tree
- Graph
- Linear
스택이 LIFO 또는 FILO 였다면 큐는 FIFO이다. 큐에 대해서 알아보자.
참고로 큐는 여러번으로 나누어서 설명할 예정이다. Deque(Double Ended Queue)라고 불리는 것도 있기 때문이다.
큐
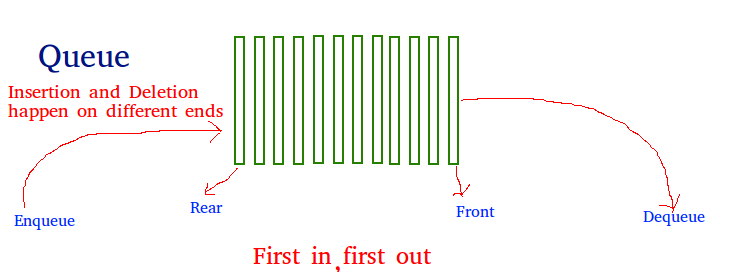
큐도 스택처럼 선형 구조이기에 실행시 순서가 있다. 순서는 FIFO(First In First Out)이다. 큐의 좋은 예로는 레스토랑이나 음식점을 생각하면 좋다. 가장 먼저온 손님이 먼저 들어가서 먼저 나온다(항상 그런것은 아니지만?).
큐와 스택의 차이점은 삭제될 때이다. 스택에서는 가장 최근에 추가된 요소가 삭제되었지만 뷰에서는 먼저 삽입된 요소부터 삭제가 된다.
큐 수행 용어
큐를 실행시킬때 사용되는 기본 작업으로는 4가지가 있다.
- 인큐(Enqueue) : 큐에 아이템을 더한다. 만약 큐가 가득 찼다면 오버플로우 상태라고 뜰 것이다.
- 디큐(Dequeue) : 큐에서 아이템을 제거한다. 아이템 제거 순서는 삽입된 순서대로 제거된다. 만약 큐가 비어있다면 언더플로우 상태라고 뜰 것이다.
- 프론트(Front) : 큐에서 앞에 있는 아이템을 갖고 온다.
- 리어(Rear) : 큐에서 마지막에 있는 아이템을 갖고 온다.
큐 구현 방법
배열과 연결 리스트를 사용해서 큐를 구현해보겠다.
배열을 이용한 큐 구현
class QueueArray {
int front, rear, size;
int capacity; // 최대 수용 용량
int array[];
// 생성자
public QueueArray(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
front = this.size = 0;
rear = capacity -1; // 왜 이렇게 넣었는지 이해가 안가지만 아마 구현할때 isFull과 isEmpty를 구현안하고 순환 반복으로 가능하게끔 해두었던거같다.
array = new int[this.capacity];
}
// 큐가 찼는지 확인; true 또는 false로 리턴
boolean isFull(QueueArray queueArray) {
return (queueArray.size == queueArray.capacity);
}
// 큐가 비어있는지 확인
boolean isEmpty(QueueArray queueArray) {
return (queueArray.size == 0);
}
// 인큐
void enqueue(int item) {
if (isFull(this)) return; // 만약 큐가 찼으면 리턴
this.rear = (this.rear + 1) % this.capacity; // 여기서 모드를 사용함으로써 위에 있는 isFull 메서드 필요없음 또한 순환으로 가능
this.array[this.rear] = item; // capacity에서 1을 뺀거를 다시 더한 후에 %한거니까 0이 나옴. 0부터 배열 시작
this.size = this.size + 1; // 현재 사이즈가 어디까지 갔는지 알려주기 위함
System.out.println(item + " enqueued to queue");
}
int dequeue() {
if (isEmpty(this)) return Integer.MIN_VALUE; // 이 ㅅㅂ; Integer.Min_VALUE 존나 좋아하네 C++ 쟁이 새끼들
int item = this.array[this.front]; // 리턴 시킬 변수에 가장 앞에 있는 값 넣기
this.front = (this.front + 1) % this.capacity; // 가장 앞에 있던 값 다음 값을 앞으로 땡기기 굳이 모드를 사용할 필요는 없다.
this.size = this.size - 1; // 하나 뺐으니 크기 -1
return item;
}
int front() {
if (isEmpty(this)) return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
return this.array[this.front];
}
int rear() {
if (isEmpty(this)) return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
return this.array[this.rear];
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
QueueArray queueArray = new QueueArray(1000);
queueArray.enqueue(10);
queueArray.enqueue(20);
queueArray.enqueue(30);
queueArray.enqueue(40);
System.out.println(queueArray.dequeue() + " dequeued from queue");
System.out.println("Front item is " + queueArray.front());
System.out.println("Rear item is " + queueArray.rear());
}
}
장점 : 구현하기가 쉽다.
단점 : 정적 자료 구조이기에 크기가 고정되어있다. 또한 대량의 enqueue 또는 dequeue가 실행될 때, 큐가 비어있더라도 실행이 안될 수도 있다(이 문제는 순환 큐를 만듬으로 피할 수 있다).
연결 리스트를 이용한 큐 구현
class QueueNode {
int node;
QueueNode next;
public QueueNode(int node) {
this.node = node;
this.next = null;
}
}
class QueueLinkedList {
QueueNode front, rear;
public QueueLinkedList() {
this.front = this.rear = null;
}
void enqueue(int node) {
QueueNode tmp = new QueueNode(node);
if (this.rear == null) return this.front = this.rear = tmp;
this.rear.next = tmp;
this.rear = tmp;
}
void dequeue() {
if (this.front == null) return;
QueueNode tmp = this.front;
this.front = this.front.next;
if (this.front == null) this.rear = null;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
QueueLinkedList queueLinkedList = new QueueLinkedList();
queueLinkedList.enqueue(10);
queueLinkedList.enqueue(20);
queueLinkedList.dequeue();
queueLinkedList.dequeue();
queueLinkedList.enqueue(30);
queueLinkedList.enqueue(40);
queueLinkedList.enqueue(50);
queueLinkedList.dequeue();
System.out.println("QueueLinkedList Front : " + queueLinkedList.front.node);
System.out.println("QueueLinkedList Rear : " + queueLinkedList.rear.node);
}
}
이것으로 큐에 대해서 개념과 구현을 해보았다. 이와 연관해서 자바의 큐 인터페이스 그리고 큐 인터페이스를 구현해주는 구현체 클래스에 대해서 알아보겠다.